SLUMP TEST OF CONCRETE AND ITS PROCEDURE
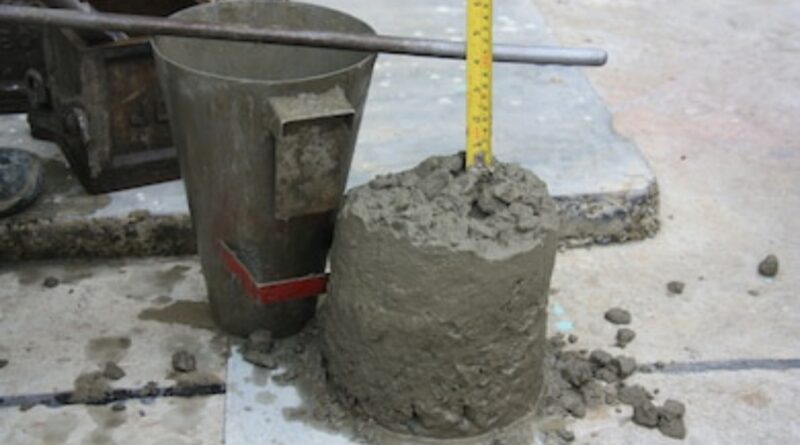
Concrete slump test is to determine the work-ability or consistency of concrete mix prepared at the laboratory or the construction site during the progress of the work. concrete slump value is used to find the work-ability, which indicates water-cement ratio
Concrete slump test is carried out from batch to batch to check the uniform quality of concrete during construction. This test is most widely used due to the simplicity of apparatus and simple test procedure. In the slump test, work-ability of concrete is not measured directly.

The slump is carried out as per procedures mentioned in ASTM C143 in the United States, IS: 1199 – 1959 in India and EN 12350-2 in Europe.
TYPES OF SLUMP:
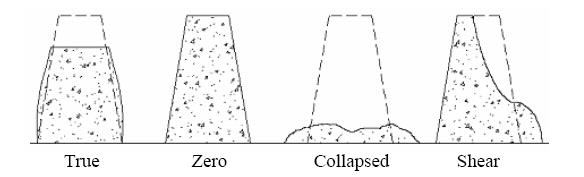
True Slump: The concrete mass after the test when slumps evenly all around without disintegration is called the true slump.
Shear Slump: When one-half of the concrete mass slide down the other is called the shear slump. This type of slump is obtained in a lean concrete mix.
Collapse Slump: When the sample is collapsed due to adding excessive water, it is known as collapse slump.
Zero Slump : Zero slump is the indication of very low water-cement ratio, which results in dry mixes. These type of concrete is generally used for road construction.
According to European Standard ENV 206: 1992, work-ability is classified in 4 categories :
- S 1: 10-40 mm
- S 2: 50-90 mm
- S 3: 100-150 mm
- S 4: more than 160 mm
Procedure
Step 1
Internal surface of the mould is cleaned carefully. Shuttering Oil can be applied on the surface.
Step 2
The mould is then placed on a base plate. The base plate should be clean, smooth, horizontal and non-porous.
Step 3
The mould is filled with fresh concrete in three layers. Each layer is tamped 25 times with a 16 mm steel rod. The rod is rounded at the ends. The tamping should be done uniformly.
Step 4
After filling the mould, excess concrete should be removed and the surface should be leveled. When the mould is filled with fresh concrete, the base of the mould is held firmly by handles.
Step 5
Then the mould is lifted gently in the vertical direction and then unsupported concrete will slump. The decrease in height at the center point is measured to nearest 5 mm and it is known as ‘slump’
| Types Of Concrete | Slump Range In mm |
| 1. Heavy mass construction | 25-50 |
| 2. Pavements | 20-30 |
| 3. Bridge deck | 25-75 |
| 4. Beams and slabs | 50-100 |
| 5. Columns, retaining walls and thin vertical members etc. | 75-150 |
| 6. Vibrated concrete | 12-25 |

